[{"countryCode":"ar","countryName":"Argentina","managerCountryCode":"ar"},{"countryCode":"au","countryName":"Australia","managerCountryCode":"au"},{"countryCode":"at","countryName":"Austria","managerCountryCode":"at"},{"countryCode":"bh","countryName":"Bahrain","managerCountryCode":"ae"},{"countryCode":"by","countryName":"Belarus","managerCountryCode":"by"},{"countryCode":"be","countryName":"Belgium (Flanders)","managerCountryCode":"nl"},{"countryCode":"br","countryName":"Brazil","managerCountryCode":"br"},{"countryCode":"bg","countryName":"Bulgaria","managerCountryCode":"ro"},{"countryCode":"kh","countryName":"Cambodia","managerCountryCode":"th"},{"countryCode":"ca","countryName":"Canada","managerCountryCode":"ca"},{"countryCode":"cl","countryName":"Chile","managerCountryCode":"cl"},{"countryCode":"cn","countryName":"China","managerCountryCode":"cn"},{"countryCode":"co","countryName":"Colombia","managerCountryCode":"pe"},{"countryCode":"cr","countryName":"Costa Rica","managerCountryCode":"cr"},{"countryCode":"hr","countryName":"Croatia","managerCountryCode":"si"},{"countryCode":"cz","countryName":"Czech Republic","managerCountryCode":"cz"},{"countryCode":"dk","countryName":"Denmark","managerCountryCode":"dk"},{"countryCode":"ec","countryName":"Ecuador","managerCountryCode":"pe"},{"countryCode":"eg","countryName":"Egypt","managerCountryCode":"eg"},{"countryCode":"sv","countryName":"El Salvador","managerCountryCode":"sv"},{"countryCode":"ee","countryName":"Estonia","managerCountryCode":"lt"},{"countryCode":"fi","countryName":"Finland","managerCountryCode":"fi"},{"countryCode":"fr","countryName":"France","managerCountryCode":"fr"},{"countryCode":"de","countryName":"Germany","managerCountryCode":"de"},{"countryCode":"gr","countryName":"Greece","managerCountryCode":"gr"},{"countryCode":"gt","countryName":"Guatemala","managerCountryCode":"gt"},{"countryCode":"hn","countryName":"Honduras","managerCountryCode":"hn"},{"countryCode":"hu","countryName":"Hungary","managerCountryCode":"hu"},{"countryCode":"in","countryName":"India","managerCountryCode":"in"},{"countryCode":"id","countryName":"Indonesia","managerCountryCode":"id"},{"countryCode":"ie","countryName":"Ireland","managerCountryCode":"gb"},{"countryCode":"il","countryName":"Israel","managerCountryCode":"il"},{"countryCode":"it","countryName":"Italy","managerCountryCode":"it"},{"countryCode":"jp","countryName":"Japan","managerCountryCode":"jp"},{"countryCode":"kz","countryName":"Kazakhstan","managerCountryCode":"kz"},{"countryCode":"ke","countryName":"Kenya","managerCountryCode":"in"},{"countryCode":"kw","countryName":"Kuwait","managerCountryCode":"kw"},{"countryCode":"la","countryName":"Laos","managerCountryCode":"th"},{"countryCode":"lv","countryName":"Latvia","managerCountryCode":"lt"},{"countryCode":"lb","countryName":"Lebanon","managerCountryCode":"lb"},{"countryCode":"lt","countryName":"Lithuania","managerCountryCode":"lt"},{"countryCode":"lu","countryName":"Luxembourg","managerCountryCode":"fr"},{"countryCode":"my","countryName":"Malaysia","managerCountryCode":"my"},{"countryCode":"mx","countryName":"Mexico","managerCountryCode":"mx"},{"countryCode":"md","countryName":"Moldavia","managerCountryCode":"ro"},{"countryCode":"ma","countryName":"Morocco","managerCountryCode":"ma"},{"countryCode":"mm","countryName":"Myanmar","managerCountryCode":"th"},{"countryCode":"nl","countryName":"Netherlands","managerCountryCode":"nl"},{"countryCode":"nz","countryName":"New Zealand","managerCountryCode":"nz"},{"countryCode":"ni","countryName":"Nicaragua","managerCountryCode":"ni"},{"countryCode":"no","countryName":"Norway","managerCountryCode":"no"},{"countryCode":"om","countryName":"Oman","managerCountryCode":"ae"},{"countryCode":"pk","countryName":"Pakistan","managerCountryCode":"pk"},{"countryCode":"pe","countryName":"Peru","managerCountryCode":"pe"},{"countryCode":"ph","countryName":"Philippines","managerCountryCode":"ph"},{"countryCode":"pl","countryName":"Poland","managerCountryCode":"pl"},{"countryCode":"pt","countryName":"Portugal","managerCountryCode":"es"},{"countryCode":"qa","countryName":"Qatar","managerCountryCode":"ae"},{"countryCode":"ro","countryName":"Romania","managerCountryCode":"ro"},{"countryCode":"ru","countryName":"Russia","managerCountryCode":"ru"},{"countryCode":"sa","countryName":"Saudi Arabia","managerCountryCode":"sa"},{"countryCode":"rs","countryName":"Serbia","managerCountryCode":"rs"},{"countryCode":"sk","countryName":"Slovakia","managerCountryCode":"sk"},{"countryCode":"si","countryName":"Slovenia","managerCountryCode":"si"},{"countryCode":"za","countryName":"South Africa","managerCountryCode":"za"},{"countryCode":"kr","countryName":"South Korea","managerCountryCode":"kr"},{"countryCode":"es","countryName":"Spain","managerCountryCode":"es"},{"countryCode":"lk","countryName":"Sri Lanka","managerCountryCode":"in"},{"countryCode":"se","countryName":"Sweden","managerCountryCode":"se"},{"countryCode":"ch","countryName":"Switzerland","managerCountryCode":"ch"},{"countryCode":"th","countryName":"Thailand","managerCountryCode":"th"},{"countryCode":"tn","countryName":"Tunisia","managerCountryCode":"tn"},{"countryCode":"tr","countryName":"Türkiye","managerCountryCode":"tr"},{"countryCode":"ua","countryName":"Ukraine","managerCountryCode":"ua"},{"countryCode":"ae","countryName":"United Arab Emirates","managerCountryCode":"ae"},{"countryCode":"gb","countryName":"United Kingdom","managerCountryCode":"gb"},{"countryCode":"vn","countryName":"Vietnam","managerCountryCode":"vn"},{"countryCode":"us","countryName":"USA","managerCountryCode":"us"},{"countryCode":"ba","countryName":"Bosnia-Herzegovina","managerCountryCode":"ba"},{"countryCode":"bew","countryName":"Belgium (Wallonia)","managerCountryCode":"fr"},{"countryCode":"dz","countryName":"Algeria","managerCountryCode":"dz"}]
[{"address":"
Robatech AG
","city":"5630 Muri AG","code":"ch","countryName":"Switzerland","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.ch","phone":"+41 56 675 77 00","qrCode":null,"street":"
Pilatusring 10
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en/contact-robatech"},{"address":"
Unique PI Sarl","city":"
Promotion SOMACOB BT. A1. N°18, 06000 Bejaia, Algérie","code":"dz","countryName":"Algeria","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"mohand.bouaichi@upi-gr.com","phone":"+213 34 12 06 70*","qrCode":null,"street":"
Mohand Bouaichi
\n
Zone industrielle Boulevard TIKAMIRA
","web":"https://upi-gr.com/"},{"address":"
UHLIG Representaciones S.R.L.
","city":"
Caseros, Prov. de Buenos Aires 1678
","code":"ar","countryName":"Argentina","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@uhligsrl.com.ar","phone":" +54 11 4734 1593","qrCode":null,"street":"
General Hornos 1307
","web":"https://www.uhligsrl.com.ar"},{"address":"
Robatech Australia Pty. Ltd.
","city":"
Silverwater NSW 2128
Australia
","code":"au","countryName":"Australia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"infodesk@robatech.com.au","phone":" +61 2 9748 4559","qrCode":null,"street":"
PO BOX 7064
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-au/australia"},{"address":"
Robatech Austria GmbH","city":"
A-3494 Theiß
","code":"at","countryName":"Austria","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"office@robatech.at","phone":" +43 2735 36901 0","qrCode":null,"street":"
Im Wirtschaftspark 7
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/de-at/organisation-oesterreich"},{"address":"Robatech BEL","city":"
225304 Kobrin
","code":"by","countryName":"Belarus","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"robatech.BY@tut.by","phone":" +375 1642 26960","qrCode":null,"street":"
Sportivnayastr. 4 BY
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/be/belarus"},{"address":"
Ferrecker Ltda / Robatech do Brasil","city":"
BR - Curitiba - Parana
","code":"br","countryName":"Brazil","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"robatech@robatech.com.br","phone":" +55 41 3123 7200","qrCode":null,"street":"
Rua Frederico Carlos Toaldo 11
\n
CEP 82.320-360 Santa Felicidade
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/pt/brasil"},{"address":"
Robatech Canada","city":"
Bolton ON L7E 4J4
Canada
","code":"ca","countryName":"Canada","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.ca","phone":"+1 416 622 4784","qrCode":null,"street":"
110 Parr Blvd Unit 101
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-ca/organization-canada"},{"address":"
Equifar S.A.","city":"
CL - Santiago
","code":"cl","countryName":"Chile","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.cl","phone":" +56 23 2742 230","qrCode":null,"street":"
Vergara 684
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/es/robatech-chile/organizacion-chile"},{"address":"
Robatech (China) Limited
","city":"
CN - 511400 Guangzhou
P.R. China
","code":"cn","countryName":"China","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.cn","phone":" +86 20 3921 1716","qrCode":{"url":"https://f.hubspotusercontent20.net/hubfs/8586020/03-Country-Pages/China/WeChat.jpg","altText":"","height":737,"type":"image","width":734},"street":"
1-204 Industrial Building
Tian An Hi-Tech Ecological Park
No. 555 Panyu Avenue, Panyu District
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en/robatech-china"},{"address":"
Codipack R.I., S.A.","city":"
Desamparados, Patarra
CR - Desamparados, San Jose
","code":"cr","countryName":"Costa Rica","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"codipackcr@relinsa.net","phone":" +506 2274-1833","qrCode":null,"street":"
OFIBODEGAS, Bodega #13
1 km Este del Liceo de San Antonio de
","web":"https://www.relinsa.com"},{"address":"
KALETECH s.r.o.","city":"
CZ-33011 Hromnice
","code":"cz","countryName":"Czech Republic","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@kaletech.cz","phone":" +420 378 605 805","qrCode":null,"street":"
Planá 20
","web":"https://www.kaletech.cz"},{"address":"
Robatech Nordic DK ApS","city":"
DK - 8870 Langå
","code":"dk","countryName":"Denmark","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.dk","phone":" +45 86 46 14 00","qrCode":null,"street":"
Industridalen 2
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/da-dk/"},{"address":"
J. C. Scientific Commercial Co.","city":"
EG - 11361 Sheraton Cairo
","code":"eg","countryName":"Egypt","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@jcsc-eg.com","phone":" +202 2267 44 94","qrCode":null,"street":"
116 Massaken Sakr Koreish
","web":"https://www.jcsc-eg.com/"},{"address":"
Servicios Industriales Internacionales, S.A. de C.V.","city":"
SV - San Salvador
","code":"sv","countryName":"El Salvador","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"serins@relinsa.net","phone":" +503 2235-2466","qrCode":null,"street":"
Colonia Buenos Aires #4Avenida Alvarado, Casa #28","web":"https://www.relinsa.com"},{"address":"
YTM-Industrial OY
","city":"
FIN - 01720 Vantaa
","code":"fi","countryName":"Finland","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"juha.lipponen@ytm.fi","phone":" +358 290 06 230","qrCode":null,"street":"
Tiilenlyöjänkuja 9 B","web":"https://www.ytm.fi"},{"address":"
Robatech","city":"
F - 55300 Chauvoncourt
","code":"fr","countryName":"France","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.fr","phone":"+33 3 2989 3614","qrCode":null,"street":"
Route de bar le duc
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/fr-fr/france/organisation-france"},{"address":"
Robatech GmbH","city":"
DE - 65520 Bad Camberg
","code":"de","countryName":"Germany","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.de","phone":" +49 6434 94110","qrCode":null,"street":"
Im Gründchen 2
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/de-de/organisation-deutschland"},{"address":"
NCA HELLAS Ltd.","city":"
GR - 14451 Metamorphosis
","code":"gr","countryName":"Greece","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@ncahellas.gr","phone":" +30 210 2815 300","qrCode":null,"street":"
5, Polemi Str.
","web":"https://www.ncahellas.gr/"},{"address":"
Relaciones Industriales, S.A.","city":"
GT - Guatemala City
","code":"gt","countryName":"Guatemala","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"relinsa@relinsa.net","phone":" +502 2505-5300","qrCode":null,"street":"
1a. Avenida 1-07 Zona 2 El Sauce
","web":"https://www.relinsa.com"},{"address":"
Facos S. DE R.L.","city":"
HN - San Pedro Sula
","code":"hn","countryName":"Honduras","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"serinh@relinsa.net","phone":" +504 2552-6353","qrCode":null,"street":"
Barrio Guamilito 7 Calle 7-8 Ave N.O. #62
","web":"https://www.relinsa.com"},{"address":"
Robatech Hungary
","city":"
HU - 8900 Zalaegerszeg
","code":"hu","countryName":"Hungary","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"zoltan.herenyi@robatech.hu","phone":" +36 30 151 151 8","qrCode":null,"street":"
Öveges József utca 3/a
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en/robatech-hungary/organization-hungary"},{"address":"
Robatech India Pvt Ltd.
","city":"
IN - Dist Thane 421 311 Maharashtra
","code":"in","countryName":"India","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.in","phone":" +91 750 666 1880","qrCode":null,"street":"
213, E-3 Bhumi World, Mumbai Nasik Rd
Pimplas (Bhiwandi)
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-in/india"},{"address":"
Robatech Indonesia
","city":"
Ketapang Cipondoh
ID - 15146 Kota Tangerang Banten
","code":"id","countryName":"Indonesia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"martinus.rafael@robatech.co.id","phone":" +62 812 8449 9227","qrCode":null,"street":"Ruko Green Lake CBD, Green lake city, Blok G2","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-id/indonesia"},{"address":"
Itas","city":"
IL - 48091 Rosh-Ha‘ain
","code":"il","countryName":"Israel","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@itas.co.il","phone":" +97 239 026 616","qrCode":null,"street":"
Industrial Technology & Services Ltd.
8-10 Hamelacha St, Ind. Park
","web":"https://www.itas.co.il"},{"address":"
Robatech Italia s.r.l. u.s.
","city":"
IT - 47522 Cesena (FC)
","code":"it","countryName":"Italy","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.it","phone":" +39 0547 631700","qrCode":null,"street":"
Via Enrico Mattei, 71","web":"https://www.robatech.com/it-it/organizzazione-italia"},{"address":"
Robatech Japan K.K","city":"
JP - 5310061 Kita-ku, Osaka
","code":"jp","countryName":"Japan","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.jp","phone":"06 4801 4481","qrCode":null,"street":"
Katayama building
9-20, 2-chome Nagaranishi
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/ja-jp/japan"},{"address":"
UNCO JET Ltd
","city":"
KZ - Almaty 050000
","code":"kz","countryName":"Kazakhstan","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info.uncojet@uncojet.com","phone":" +7 727 381-98-24","qrCode":null,"street":"
Auezov District, Almas Microdistrict, Building 246","web":"https://www.uncojet.kz"},{"address":"
AL-Jawad Photo & Trading Co.","city":"
KW - 13046 Safat
","code":"kw","countryName":"Kuwait","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@aljawadkw.com","phone":" +965 2 483 9101","qrCode":null,"street":"
P.O. Box 4545
Sahafa Street
","web":"https://www.alsanad.org/"},{"address":"
Zakka Multitec S.A.R.L.","city":"
Maten 1202 2110
","code":"lb","countryName":"Lebanon","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@zakkamultitec.com","phone":" +961 1 890 654","qrCode":null,"street":"
Zakka Bldg, Fanar, Beirut, Lebanon
PO Box: 90 1352,
","web":"https://www.zakkamultitec.com/"},{"address":"
Robatech (M) SDN BHD","city":"
MY - Selangor
","code":"my","countryName":"Malaysia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.com.my","phone":" +603 7843 6636","qrCode":null,"street":"
No20, Jln PJU1A/13, Tmn Perindustrian Jaya, Ara Damansara,
Petaling Jaya 47301
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-my/organization-malaysia"},{"address":"
Unicode","city":"
MA - 20000 Casablanca
","code":"ma","countryName":"Morocco","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"unicode@unicode.ma","phone":" +212 522 672 522","qrCode":null,"street":"
57, Allée des Jardins
","web":"https://www.unicodemaroc.com"},{"address":"
Robatech de Mexico S.A. de C.V.","city":"
MX – Querétaro, Qro C.P. 76116
","code":"mx","countryName":"Mexico","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"robatech@robatech.com.mx","phone":"+52 442 348 1354","qrCode":null,"street":"
Av Peñaflor # 1102
Col. Ciudad del Sol
Novatec Business park Int 97-A
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/es-mx/organizacion-mexico"},{"address":"
IMH EngineeringIntelligent Material Handling","city":"
NZ - 4110 Napier
","code":"nz","countryName":"New Zealand","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@imhengineering.co.nz","phone":" +64 22 164 2126","qrCode":null,"street":"
4F/3 Shakespeare Rd
","web":"https://www.imhengineering.co.nz"},{"address":"
Codipack R.I., S.A.","city":"
NI - Managua
","code":"ni","countryName":"Nicaragua","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"relinsa@relinsa.net","phone":" +505 2299 3584","qrCode":null,"street":"
Villa Pedro Joaquín Chamorro, semáforos de la Róbelo
5 cuadras al norte ½ cuadra al oeste
","web":"https://www.relinsa.com"},{"address":"
Robatech Nordic NO AS","city":"
NO - 3511 Hønefoss
","code":"no","countryName":"Norway","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.no","phone":" +47 32 14 23 75","qrCode":null,"street":"
Hvervenmoveien 45
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/no/norge"},{"address":"
Ultratec International","city":"
PK - Lahore Cantt
","code":"pk","countryName":"Pakistan","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@ultratecpak.com","phone":" +92 321 844 83 84","qrCode":null,"street":"
4-A Abdul Rehman Road,
Imtiaz Shaheed Road
","web":"https://www.ultratecpak.com"},{"address":"
AUMPACK INC
","city":"
PH - 1780 Muntinlupa City
","code":"ph","countryName":"Philippines","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@aumpack.com","phone":"+63-2-8041588","qrCode":null,"street":"
Unit 810, Alpap II bldg., Trade Ave.
Cor. Investment Drive, Madrigal Business Park
","web":"http://www.aumpack.com"},{"address":"Robatech Polska Sp. z o.o.","city":"
PL - 44-105 Gliwice
","code":"pl","countryName":"Poland","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.pl ","phone":" +48 32 270 20 32","qrCode":null,"street":"
Ul. Żernicka 35
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/pl-pl/poland"},{"address":"
Robatech Rus LLC","city":"
RU - 197374, Saint-Petersburg
","code":"ru","countryName":"Russia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"gt@robatech.ru","phone":" +7 812 449 56 78","qrCode":null,"street":"
Business Center „Lakhta“, office 215
Optikov St., house 4, bldg. 2, A
","web":"https://www.robatech.ru"},{"address":"
Yousef Al Sanad Trading Est.","city":"
KSA - Jeddah 21484
","code":"sa","countryName":"Saudi Arabia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@alsanad.org","phone":" +966 555 840 301","qrCode":null,"street":"
P.O. Box 17305
Tahlia Street
","web":"https://www.alsanad.org"},{"address":"
MB Print d.o.o.","city":"
RS - 21235 Temerin
","code":"rs","countryName":"Serbia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"office@mbprint.eu","phone":"+381 21 844 400","qrCode":null,"street":"
Novosadska 280
","web":"https://www.mbprint.eu/"},{"address":"
Robatech SA (Pty) Ltd (Western Cape)","city":"
ZA - Cape Town 7405
","code":"za","countryName":"South Africa","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.co.za","phone":"+27 21-510 6903","qrCode":null,"street":"
24 Shropshire Street
Paarden Eiland
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-za/south-africa/organization"},{"address":"SETEC Korea","city":"
KR - 133-120 Seoul
","code":"kr","countryName":"South Korea","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"robatech@robatech.co.kr","phone":"+82 2 971 0471","qrCode":null,"street":"
Room No. 203, IS Biz Tower, 147 SeongSu-2Ro
SeongDong-Gu
","web":null},{"address":"
Robatech Nordic AB","city":"
SE - 302 62 Halmstad
","code":"se","countryName":"Sweden","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.se","phone":"+46 35 299 0510","qrCode":null,"street":"
Ryttarevägen 18B
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/sv/sverige"},{"address":"
JETS","city":"
TN - Tunis 1082
","code":"tn","countryName":"Tunisia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"jets@gnet.tn","phone":" +216 71 235 518","qrCode":null,"street":"
Tour des bureaux ICC Agence 04 RDC
Centre Urbain Nord
","web":"https://jets-tn.com/"},{"address":"
Robatech Tutkal Teknolojileri Sanayi ve Ticaret A. Ş.","city":"
TR - 41040 İzmit - Kocaeli
","code":"tr","countryName":"Türkiye","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.com.tr","phone":"+90 262 322 41 57","qrCode":null,"street":"
Sanayi Mah. Kozalı Sok. No: 10 Çarşı Yapı
Sitesi C33
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/tr-tr/organizasyon-turkiye"},{"address":"
RO Technologies","city":"
UA - Kiev 04111
","code":"ua","countryName":"Ukraine","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.com.ua","phone":"+380 68 224 66 42","qrCode":null,"street":"
Danila Schbakivskogo st. 52, 429,
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/uk/ukraine"},{"address":"
Robatech Gluing Technology","city":"
Essex SS15 6SW
United Kingdom
*Robatech Gluing Technology is an
authorized trading name of W. H. Leary Ltd.
","code":"gb","countryName":"United Kingdom","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatechGT.com","phone":"+44 1268 490035","qrCode":null,"street":"
2 Seax Way, Basildon
","web":"www.robatech.com/en-gb/great-britain"},{"address":"
Robatech USA Inc.","city":"
Alpharetta, GA 30005 USA
","code":"us","countryName":"USA","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatechusa.com","phone":"+1 770 663 8380","qrCode":null,"street":"
1005 Alderman Drive Ste 207
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en-us/organization-usa"},{"address":"
Vinatech Co., Ltd.","city":"
Ho Chi Minh City, VN - 727010 HCM
","code":"vn","countryName":"Vietnam","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@vinatech.biz","phone":"+84 28 3601 8068","qrCode":null,"street":"
38 Street 2 - Cityland, An Nhon ward
","web":"https://www.vinatech.biz"},{"address":"
Robatech Gulf FZE
","city":"
UAE – Sharjah","code":"ae","countryName":"United Arab Emirates","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.ae","phone":"+971 562 55 4966","qrCode":null,"street":"
Sharjah Airport Free Zone
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en/robatech-united-arab-emirates"},{"address":"
UAB Tecalemit
","city":"
LT - 02189, Vilnius
","code":"lt","countryName":"Lithuania","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"egidijus.s@tecalemit.lt","phone":" +370 5 210 6210","qrCode":null,"street":"
Dariaus ir Gireno g. 177
","web":"https://www.tecalemit.lt"},{"address":"
Robatech bv
","city":"
NL - 6931 KE Westervoort
","code":"nl","countryName":"Netherlands","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.nl","phone":"+31 26 319 01 10","qrCode":null,"street":"
Mollevite 5
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/nl/nederland"},{"address":"
NOBLEKA SAC
","city":"
PE - Lima 41
","code":"pe","countryName":"Peru","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"mario.calderon@nobleka-digital.com","phone":"+51-998-308-912","qrCode":null,"street":"
Calle Bronsino 320
San Borja
","web":"https://www.nobleka.com.pe"},{"address":"
Kovacs Trade Company S.R.L
","city":"
RO - Jud. Mures
","code":"ro","countryName":"Romania","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"j.kovacs@kovacstrade.ro","phone":"+40 744 624 947","qrCode":null,"street":"
Cart. Rodnei 3/3
545300 Reghin
","web":"https://www.kovacstrade.com"},{"address":"
Robatech España, S.L.
","city":"
ES - 28021 Villaverde - Madrid
","code":"es","countryName":"Spain","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.es","phone":"+34 91 683 82 14","qrCode":null,"street":"
C/ Ciudad de Frias, 11 y 13 Nave E
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/es-es/espana/organizacion-espana"},{"address":"
iNEX Technology Co., Ltd
","city":"
TH - Bangkok 10230
","code":"th","countryName":"Thailand","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"sales@inextechnology.com","phone":"+66 2 578 8311","qrCode":null,"street":"
442 Sukhonthasawat Road
Ladprao
","web":"https://inex.co.th/"},{"address":"Robatech Austria GmbH, o.z.","city":"
81106 Bratislava
","code":"sk","countryName":"Slovakia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"jakub.buchel@robatech.sk","phone":"+421 918 514 401","qrCode":null,"street":"
Hodžovo námestie 1/A
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/sk/slovensko"},{"address":"
MB Print d.o.o. Bosna i Hercegovina","city":"
Grude, Gorica, 88345
","code":"ba","countryName":"Bosnia-Herzegovina","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"marko@mbprint.ba","phone":"+387 39 671 207","qrCode":null,"street":"
Brig 96
","web":"http://www.mbprint.ba"},{"address":"Robatech Austria GmbH - podružnica v Ljubljani","city":"1351 Brezovica pri Ljubljani","code":"si","countryName":"Slovenia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"matej.zvajkar@robatech.si","phone":"+386 41 568 573","qrCode":null,"street":"
Matej Žvajkar, Prodaja in servis
Tržaška cesta 515
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/sl/slovenija"},{"address":"
Robatech Headquarters
","city":"5630 Muri AG","code":"hq","countryName":"Headquarters","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"info@robatech.ch","phone":"+41 56 675 77 00","qrCode":null,"street":"
Pilatusring 10
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/en/contact-robatech"},{"address":"Robatech Austria GmbH - podružnica v Ljubljani","city":"1351 Brezovica pri Ljubljani","code":"hr","countryName":"Croatia","countryResponsibleFor":null,"email":"matej.zvajkar@robatech.si","phone":"+386 41 568 573","qrCode":null,"street":"
Matej Žvajkar, Prodaja in servis
Tržaška cesta 515
","web":"https://www.robatech.com/sl/slovenija"}]
 Rolf Gräser, Industry Manager Packaging
Rolf Gräser, Industry Manager Packaging
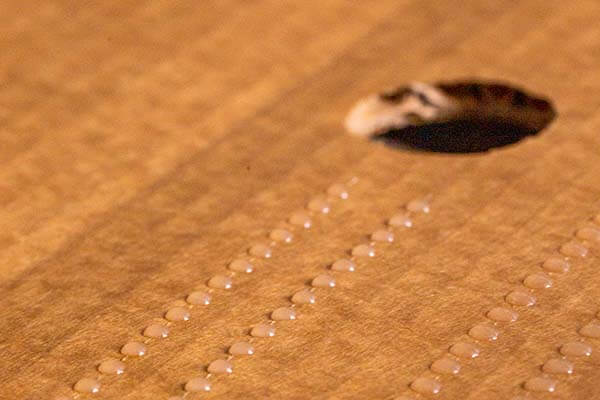

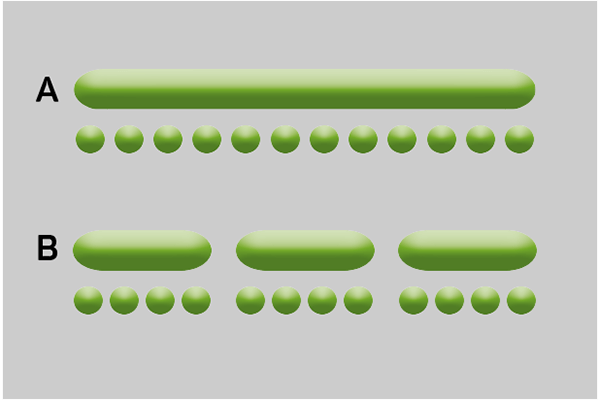 Hot melt stitching can reduce the consumption of hot melt adhesive.
Hot melt stitching can reduce the consumption of hot melt adhesive.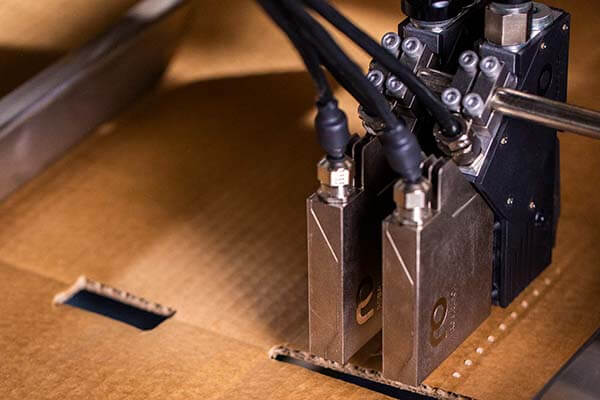  Electric application heads offer the ideal conditions for hot melt stitching.
Electric application heads offer the ideal conditions for hot melt stitching.  Adhesive savings with hot melt stitching can be accurately calculated.
Adhesive savings with hot melt stitching can be accurately calculated.  The adhesive application must meet certain criteria to ensure the recyclability of cardboard or paper.
The adhesive application must meet certain criteria to ensure the recyclability of cardboard or paper. 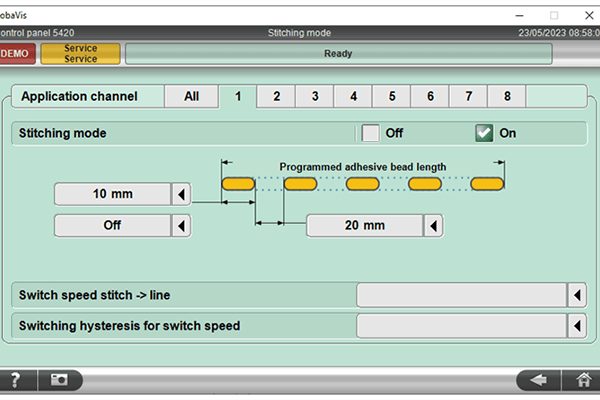 You can choose the bead length in stitching mode.
You can choose the bead length in stitching mode. 

COMMENTS
2 COMMENTS